
Increased natural lighting
Large windows, skylights, and vaulted ceilings allow natural light to penetrate deep into the building and make rooms feel light and spacious, making the spaces more livable as well as minimizing the use of electric lights during daylight hours.

Passive cooling
Buildings will be cooled during hot months using passive (nonmechanical) strategies such as: calculated shading devices (to block the entrance of sun), natural ventilation, cool roofing, and storage/emission of night cooling by thermal mass.

Passive heating
Buildings will be kept warm in the winter using passive (non-mechanical) strategies such as: calculated shading devices (allowing the entrance of the low winter sunlight), storage/emission of heat by thermal mass, and ceiling fans.

Optimized Shading
Carefully placed trellises, porches, trees, and high quality and reflective window shades provide summer shade while allowing the entrance of winter sun and ample natural light.

Increased thermal mass
Concrete floors, as well as extra thick and dense gypsum board throughout, increase the building’s thermal mass. This allows for the storage of solar energy in the winter and for the building to take advantage of night cooling during the summer.
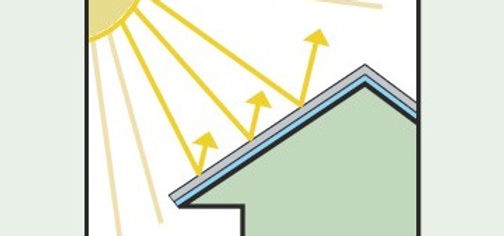
Cool roof
Cool roofs are constructed of materials that very effectively reflect the sun’s energy from the roof surface as well as having high emissivity, allowing them to emit infrared energy. The idea behind a cool roof is that it reflects and emits the sun’s heat back to the sky instead of transferring it to the building below.
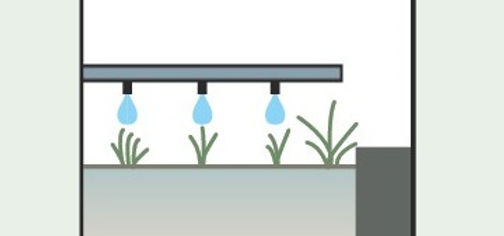
Efficient irrigation systems
All irrigation systems shall be designed to minimize the amount of water used for irrigation purposes. Systems will include drip systems, low application rate spray heads, water sensors and check valves to prevent low point drainage. Design of irrigation systems will preclude over spray onto paved areas.
Native Vegetation
Site planning, grading, and trenching shall be designed to incorporate areas of vegetation. Existing vegetation to remain shall be protected from impacts during construction. New planting will minimize the use of extensive water, fertilizers, herbicides, and provide a habitat for native bird, insect, and animal populations.

Sustainably Grown Lumber
If feasible, lumber used in the building framing will be certified “sustainably grown” by the forest stewardship council. “sustainably grown” lumber comes from forests where clear-cutting is not practiced, where logging does not damage habitats or watersheds, and where trees need to be thinned.
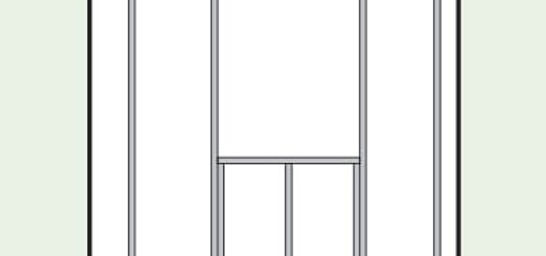
Advanced Framing
This framing style reduces the amount of wood and large dimensional lumber necessary. It uses studs @ 24” on center, minimal headers, and engineered wood members. This allows more space for insulation and higher windows heights, bringing more natural light into the space.

Deeper Wall Framing
2x6 wall framing at 24” on center creates deeper walls, allowing for better insulated walls.
Efficient Appliances, Fixtures and Finishes

Energy Star Appliances
Whenever possible, the project will use Energy Star stoves, refrigerators and dishwashers, as well as highly efficient heating systems and air conditioners.

Efficient Lighting
Compact fluorescent, halogen, and LED light fixtures are used extensively. They give off a warm, pleasant light while conserving energy. The electric bill will be minimized with the use of these light fixtures and natural light.

Efficient water heaters
High efficiency and instant water heaters will supply water to showers, faucets, and all potable water. These energy efficient units use less energy than standard water heaters and do not store hot water inside the building envelope.

Sustainable building materials
Sustainable building materials such as engineered wood, trex decking (composed of 50% recycled bottles and 50% sawdust) and concrete mixed with fly ash will be used. These are durable solutions that reduce our impact on the earth’s resources.

Sustainable flooring
Flooring will include marmoleum (a natural, low toxic true linoleum alternative to vinyl composed of 50% linseed oil and 50% cellulose), carpeting made from recycled materials, and engineered wood floors, such as bamboo.

Efficient windows
Double-pane, low-e2 glazing keeps heat inside the house from escaping during the winter and prevents heat from entering in the hot summer months, reducing the building’s energy use and keeping the houses more comfortable.

Quality wall surfaces
Thicker and denser gypsum board adds thermal mass, provides sound insulation and fire resistance, creating a safer, more pleasant living space which is cooler in summer and warmer in winter.
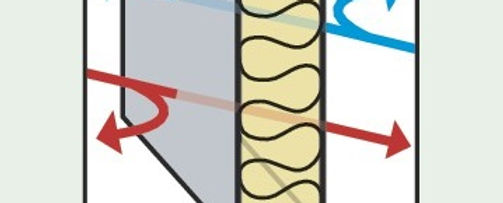
Insulation
Blown-in cellulose insulation provides levels of r22 in the walls and r38 in the ceilings. It virtually eliminates air infiltration through the envelope, whereby some studies say 55% of heat energy would otherwise be lost.

Indoor Air Quality
Non-toxic materials are used when economically feasible. these include low voc (volatile organic compounds and low formaldehyde) interior paint, water-based interior finishes, glues, wood preservatives, and marmoleum in place of vinyl.

Low-flow plumbing fixtures
Low-water-use toilets, faucets, and shower heads provide quality without wasting water.
Sustainable Community Living

Community Education
Ongoing community education is essential to the creation and maintenance of a sustainable community. Discussion and education (at least annually) on ways to reduce energy, water and resource consumption will be an integral part of community interaction and energy savings.
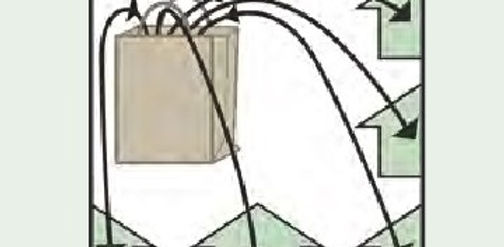
Shared Resources
Drawing from a common pool of resources, members of the community will use less and have access to more. One lawn mower for 30 homes, one pool for 30 homes, etc.

Walk to Community
Our project brings people closer to their friends and community. Necessary services will be in close proximity to the homes, lessening peoples’ dependence on automobiles and fostering a more sustainable lifestyle and community.

Recycling
By developing a community
consciousness focused on enhanced recycling, a significant amount of waste generated by the community can be kept out of landfills.

Compact Development
Development will be clustered and by definition, not sprawl.
Landscape

Deciduous trees and passive cooling
Deciduous canopy shade trees located throughout the site will help limit solar gain during summer months and will allow the entrance of light and warmth during the winter. Many new trees will be added.

Erosion and runoff control
Bioswales will be incorporated into the landscape in order to filter runoff from impermeable surfaces on the site. The time water spends flowing through the swale will be maximized so as to remove as much silt and pollutants as possible. Slowing the rate of runoff also helps to prevent erosion.

Permeable paving materials
If feasible, permeable paving materials will be used to finish some hard surfaces such as paths, common areas, and rear patios. permeable paving materials help to replenish stores of groundwater and aid in the management of erosion and pollution by permitting the slow infiltration of stormwater runoff into underlying soil.

Decomposed granite surfaces
When feasible, pathways will have dg (decomposed granite) surfaces. Decomposed granite can be compacted to create a smooth surface with good drainage/infiltration to the underlying soil. The light color of dg also promotes reflectance which helps to diminish the “heat island effect.”

Dark sky lighting
Exterior light fixtures will be chosen that contribute as little light pollution as possible to the night sky.